There is still a race in progress which of the window joinery manufacturers will achieve a better air exchange rate. Of course, all of this has to do with the economy. The more airtight our building is, the less money we spend on heating it by reducing heat loss. Therefore, everyone strives to make a thermos of their home.
For many years, the designers used to assume that fresh air enters the flats through the gaps between the window sash and the frame, between the frame and the wall, between the window pane and the wooden frame. The problems began when high-quality windows with sophisticated fittings and glass panes appeared on the market, which until recently had been unimaginable in terms of insulation.
It is a paradox that better materials are used to create buildings that are less human-friendly. Research conducted in the West on the Sick Building Syndrome has confirmed that the main cause of illnesses among people living in such buildings is poor air quality. If not properly ventilated, it is chemically and biologically contaminated to a catastrophic extent.
A significant reduction in the construction time of a house from 5-7 years in the 70s to 2-3 years at the end of the 90s resulted in the new building often not managing to get rid of the substances and chemical compounds contained in the materials used in its construction, as well as water present in the foundations, walls and ceilings.
Contrary to appearances, the situation deteriorates when we start a gas kitchen. During combustion, gas extracts oxygen from the air and releases carbon dioxide and water vapour into the environment, which are the natural products of its combustion.
This results in damp walls, misty windows, wet towels in the bathroom, wallpaper falling off, mould, stuffy air, malodour and unpleasant smells that permeate our clothes, as well as bad mood and general irritation caused by excess carbon dioxide and lack of oxygen in the surrounding air. We are often troubled by allergic hypersensitivity, which is also a result of the lack of proper ventilation in our homes.
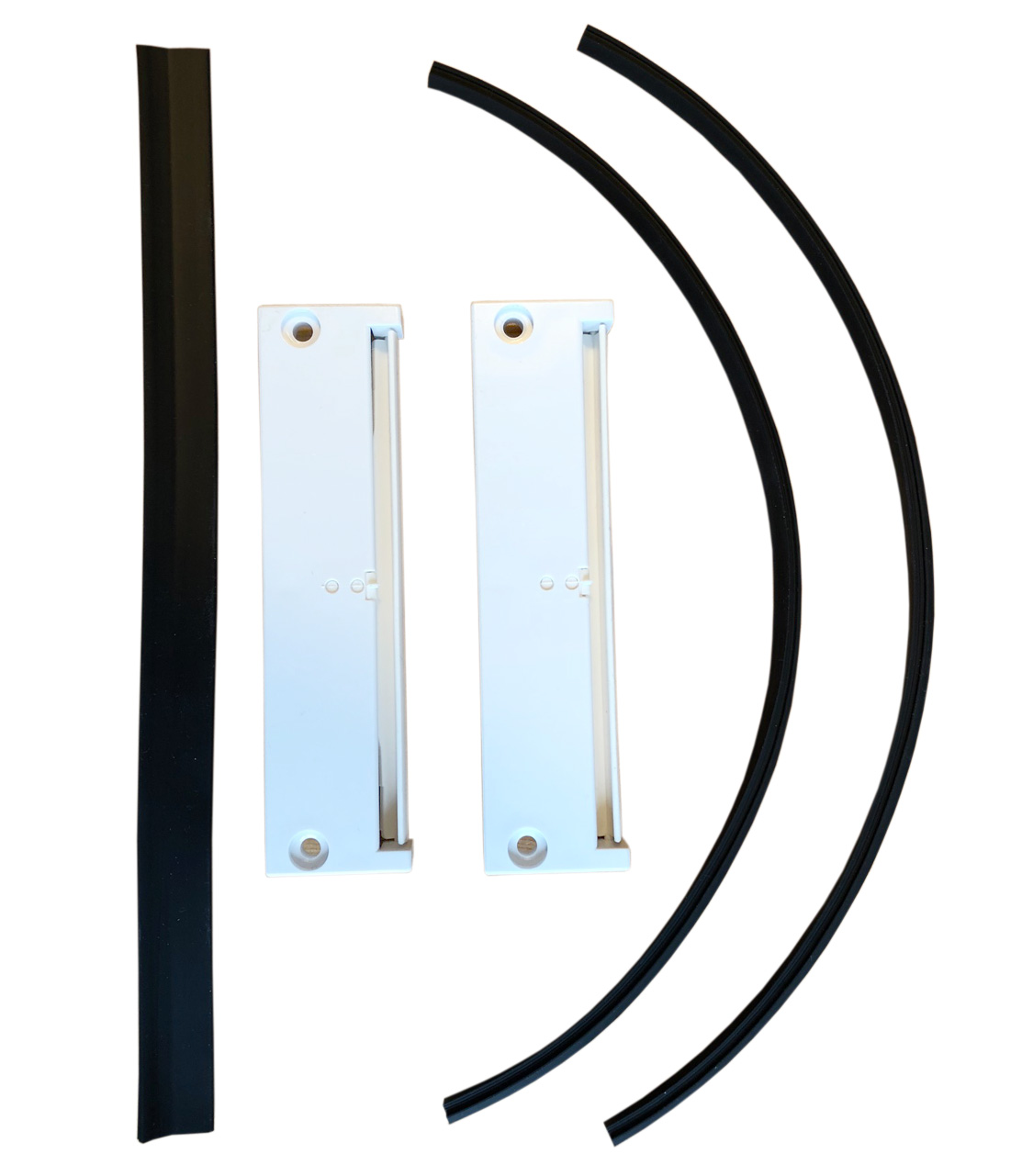
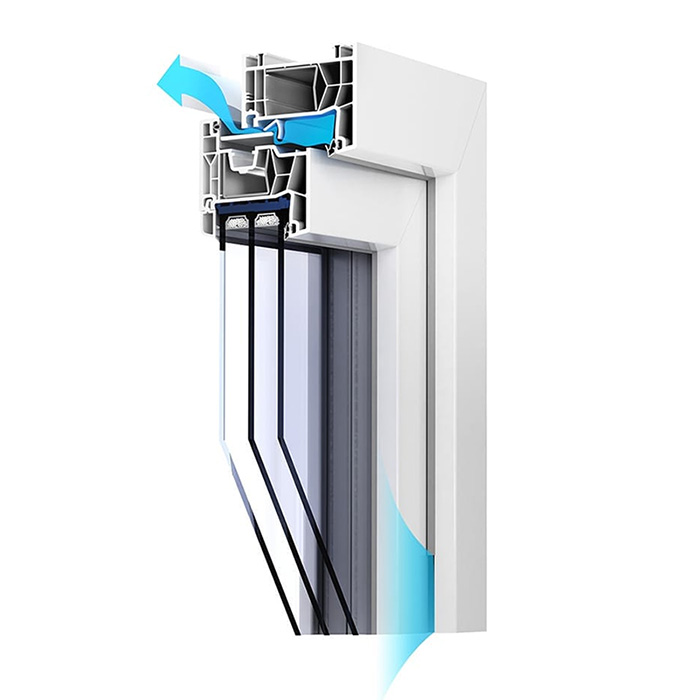
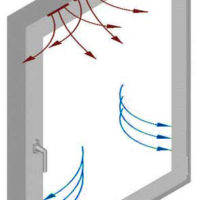
In modern countries, which earlier than Poland realised the need to save energy and replace used windows with state-of-the-art, more airtight ones, the issues of healthy living and health protection are strongly emphasized. Window air vents are commonly used there, the so-called compact window ventilators. They are located in the upper part of the window (in the frame), as a result of which fresh air enters the room, forcing the action of gravity ventilation and removing stale and damp air from the room.